11.14.线性回归
Windows 10
Python 3.7.3 @ MSC v.1915 64 bit (AMD64)
Latest build date 2020.11.03
sklearn version: 0.23.1
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from toolkit import H
import numpy as np
from scipy import linalg
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error, r2_score
from sklearn.linear_model import (LinearRegression,
Ridge,
SGDRegressor)
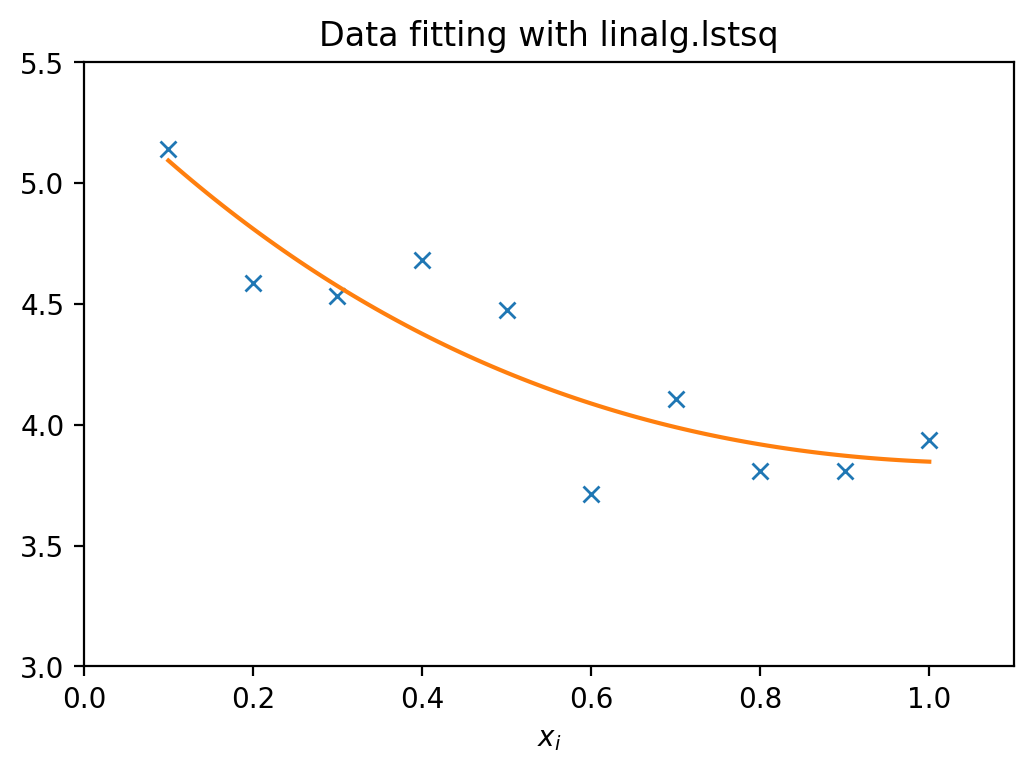
求解二乘最小问题
$$ y = c_1 \times e^{-x} + c_2 \times x $$
$$ z = y + \varepsilon $$
$$ \boldsymbol{A} = \left(\boldsymbol{e^{-x}}, \boldsymbol{x} \right)\qquad $$
# 设定真实函数的参数
c1, c2 = 5.0, 2.0
# 生成函数的自变量 X
X = np.r_[0.1:1.1:0.1]
# 设置真实函数
y = c1 * np.exp(-X) + c2 * X
# 目标函数:真实函数 + 随机干扰
z = y + 0.05 * np.max(y) * np.random.randn(len(y))
# A 是自变量矩阵
A = np.c_[np.exp(-X)[:, np.newaxis], X[:, np.newaxis]]
print(f"系数矩阵 A:\n{A}")
# 求解最小二乘 A*c = z
c, mse, rank, sigma = linalg.lstsq(A, z) # 解 均方差 秩
print(f"Parameters estimated by Least Squares: c1={c[0]:.3f}\tc2={c[1]:.3f}")
print(f"Real parameters: c1={c1}\tc2={c2}")
# 利用估计参数计算z的预测值
z_pred = c[0] * A[:, 0] + c[1] * A[:, 1]
lstsq_mse = np.mean(np.square(z - z_pred))
print(f"Mean squared error: {lstsq_mse}")
系数矩阵 A:
[[0.90483742 0.1 ]
[0.81873075 0.2 ]
[0.74081822 0.3 ]
[0.67032005 0.4 ]
[0.60653066 0.5 ]
[0.54881164 0.6 ]
[0.4965853 0.7 ]
[0.44932896 0.8 ]
[0.40656966 0.9 ]
[0.36787944 1. ]]
Parameters estimated by Least Squares: c1=5.425 c2=1.852
Real parameters: c1=5.0 c2=2.0
Mean squared error: 0.03904797048010764
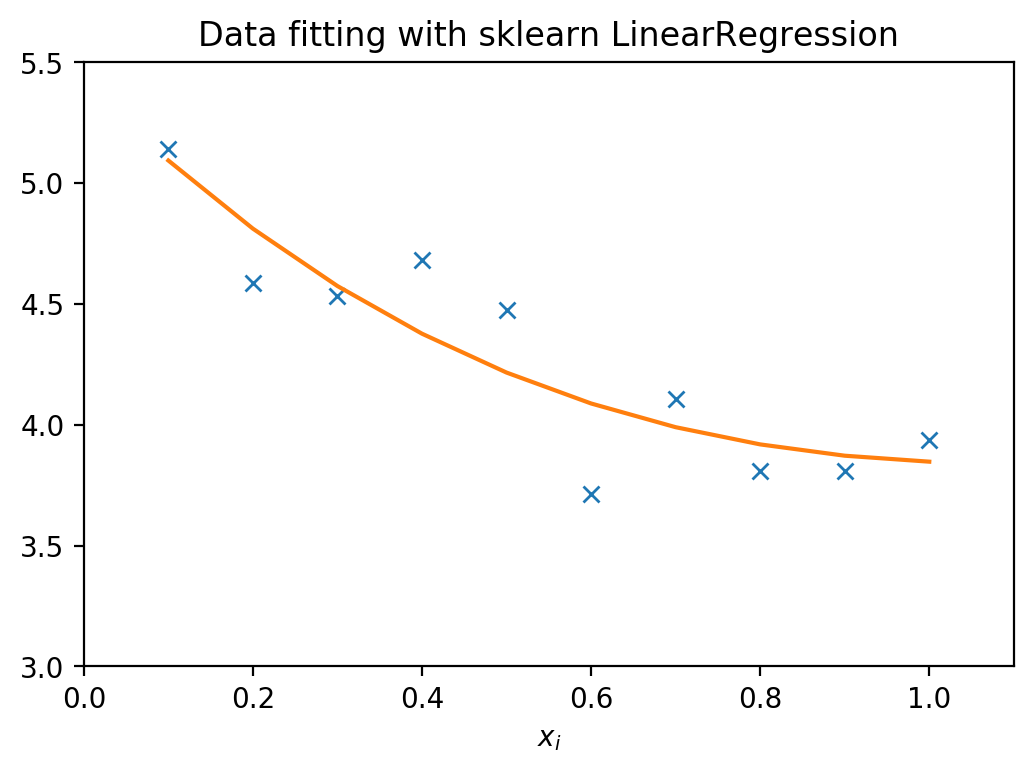
LinearRegression
LinearRegression(fit_intercept=True, normalize=False, copy_X=True,
n_jobs=None)
参数
fit_intercept:布尔值。是否计算线性回归中的截距。normalize:布尔值。如果为True,那么训练样本将使用L2范数进行归一化。fit_intercept=False时忽略该参数。copy_X:布尔值。是否复制X,不复制的话可能会改写X变量。n_jobs:整数。指定任务并行时使用的CPU数量,如果取值为-1则使用所有可用的CPU。
属性
coef:权重向量intercept_:截距
方法
fit(X,y):训练模型。predict(X):预测。score(X,y):评分,计算公式为$\text{score} = R^2 = 1 - \frac{\sum(y - \hat{y})^2}{\sum(y - \bar{y})^2}$。score最大值是1,但有可能是负值(预测效果太差)。score越大,预测性能越好。
# Create linear regression object
regress_model = LinearRegression(fit_intercept=False, normalize=False)
# Train the model using the training sets
regress_model.fit(A, z)
# Make predictions using the testing set
z_pred = regress_model.predict(A)
sklearn_mse = np.mean(np.square(z-z_pred))
# The coefficients
print(f'Parameters estimated by LinearRegression: {regress_model.coef_}')
# The mean squared error
print('Mean squared error: %.2f' % mean_squared_error(z, z_pred))
# The coefficient of determination: 1 is perfect prediction
print('Coefficient of determination: %.2f' % r2_score(z, z_pred))
Parameters estimated by LinearRegression: [5.42512871 1.85174901]
Mean squared error: 0.04
Coefficient of determination: 0.81
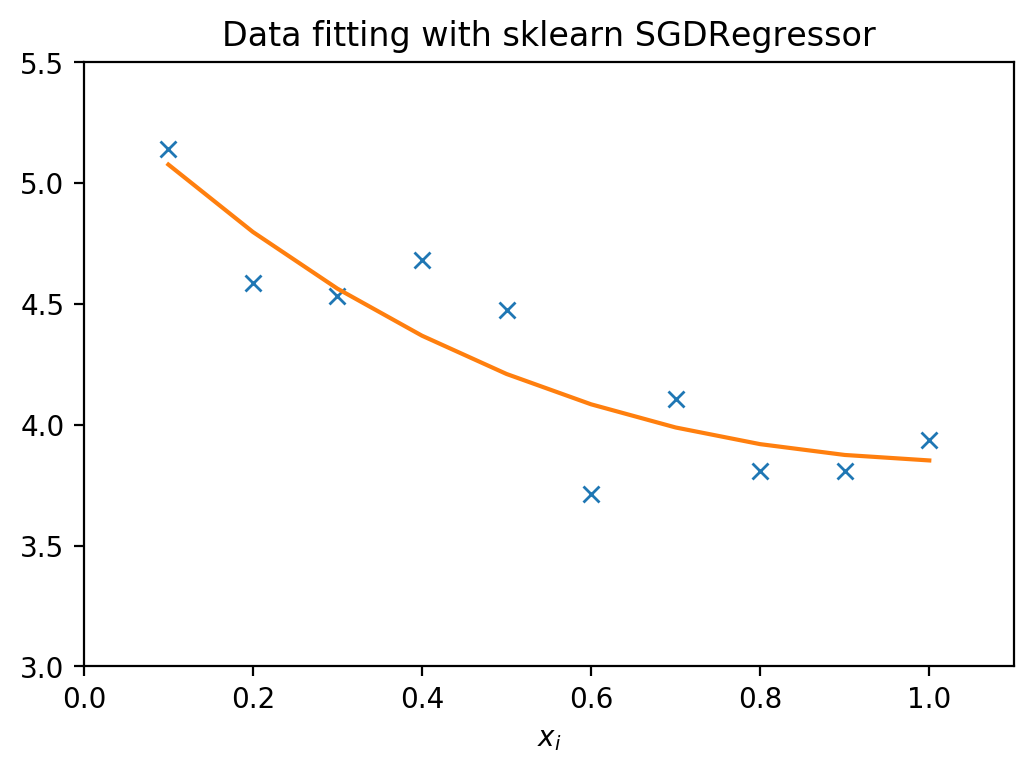
SGDRegressor
SGDRegressor(loss='squared_loss', penalty='l2', alpha=0.0001,
l1_ratio=0.15, fit_intercept=True, max_iter=1000,
tol=0.001, shuffle=True, verbose=0, epsilon=0.1,
random_state=None, learning_rate='invscaling', eta0=0.01,
power_t=0.25, early_stopping=False,
validation_fraction=0.1, n_iter_no_change=5,
warm_start=False, average=False)
loss:要使用的损失函数。可能的值为"squared_loss","huber","epsilon_insensitive","squared_epsilon_insensitive"。penalty:正则项。可能的值为"l2","l1","elasticnet",默认为"l2"。alpha:与正则项相乘的常数。值越高,正则化越强。默认为0.0001。l1_ratio: Elastic 网络混合参数。取值范围为0 <= l1_ratio <= 1。1_ratio=0相当于L2正则项,1_ratio=1相当于L1正则项。仅在penalty='elasticnet'时有效。fit_intercept:是否应该估计截距。如果为False,则假定数据已经中心化。max_iter:训练集的最大迭代次数,又称为epochs,它只会影响fit方法中的行为,而不会影响partial_fit方法。tol:停止准则。如果非None,则当 loss > best_loss - tol 持续n_iter_no_change次迭代后,训练将停止。shuffle:在每个epoch之后是否应重新对训练数据进行洗牌。epsilon:epsilon-insensitive 损失函数中的Epsilon ,仅当loss为"huber","epsilon_insensitive","squared_epsilon_insensitive"时有效。-
learning_rate:学习率调整策略。可能的值为:-
"constant":eta = eta0 -
"optimal":eta = 1.0 / (alpha * (t + t0))其中t0由Leon Bottou提出的启发式方法选择。 -
"invscaling":eta = eta0 / pow(t, power_t) -
"adaptive": eta = eta0
-
-
eta0:学习率。 early_stopping:当验证分数没有提高时,是否使用提前停止来终止培训。如果设置为 True,它将自动留出一部分训练数据作为验证,并在score方法返回的验证得分至少n_iter_no_change个epoch没有减少tol时终止训练。validation_fraction:预留的验证集的比例。仅在early_stopping为True时使用。
sgd_regression_model = SGDRegressor(loss='squared_loss',
fit_intercept=False, max_iter=10000,
alpha=0.001, validation_fraction=0.3)
sgd_regression_model.fit(A, z)
print(f'Coefficients: {sgd_regression_model.coef_}')
Coefficients: [4.11459251 2.76786944]
如果训练集样本量太少,即使增加epoch的大小,也难以拟合。以下对训练集进行过采样。
repeat_num = 10000
new_A = np.concatenate([A]*repeat_num)
new_z = np.concatenate([z]*repeat_num)
sgd_regression_model.fit(new_A, new_z)
# Make predictions using the testing set
z_pred = sgd_regression_model.predict(A)
# The coefficients
print(f'Coefficients: {sgd_regression_model.coef_}')
# The mean squared error
print('Mean squared error: %.2f' % mean_squared_error(z, z_pred))
# The coefficient of determination: 1 is perfect prediction
print('Coefficient of determination: %.2f' % r2_score(z, z_pred))
Coefficients: [5.4053131 1.86414048]
Mean squared error: 0.04
Coefficient of determination: 0.81
手动实现SGDRegressor
import numpy as np
class SGDRegressorSimple:
def __init__(self, learn_ratio=0.001, max_iter=1000):
self.learn_ratio = learn_ratio
self.max_iter = max_iter
self.C = None
def _calculate_gradient(self, X, Y):
step = self.learn_ratio * np.sum((np.dot(A, self.C) - Y) * A, axis=0)
step = step.reshape(self.C.shape)
self.C -= step
def fit(self, X, y):
Y = np.array(y)
X = np.array(X)
if len(Y.shape) == 1:
Y = Y.reshape(-1, 1)
elif len(Y.shape) != 2:
raise ValueError("the shape of Y must be 2 dim")
if len(X.shape) != 2:
raise ValueError("the shape of X must be 2 dim")
Y_shape = Y.shape
X_shape = X.shape
if self.C is None:
self.C = np.zeros((X_shape[1], 1))
C_shape = self.C.shape
if X_shape[0] != Y_shape[0]:
raise ValueError("the length of X and y are not equal")
if X_shape[1] != C_shape[0]:
raise ValueError("X.shape[1] is not equal to C.shape[1]")
for i in range(self.max_iter):
self._calculate_gradient(X, Y)
sgd = SGDRegressorSimple(learn_ratio=0.01, max_iter=1000)
sgd.fit(A, y)
print(f'Coefficients: {sgd.C.flatten()}')
Coefficients: [4.9999651 2.00003525]